Blooms Taxonomy
# Reference
- Source: #EDUC101i #EDUC130_3
- Keywords: Cards/permanent notes
- #education #teaching #learning
- Relevant Notes:
# Notes
Created by educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom
Not all learning objectives are created equal. By determining the level by which a learning objective is in, we can make sure that your learning objectives help deepen a students’ understanding and ability.
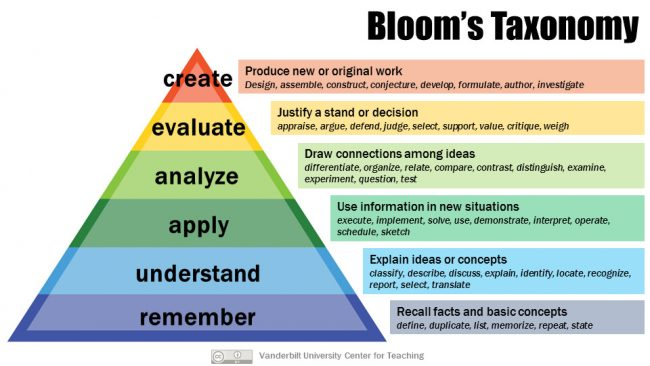
The upper part of the taxonomy involved learning objectives that fell in the category “higher order thinking” while objectives that target the lower part of the taxonomy were those of “lower order thinking”.
According to Borich, one way we can distinguish these two broad categories of objectives is to say that"
- what needs to be taught to meet lower order objectives (Understand and Remember) are often **"==facts, rules and action sequences== (or what Borich refers to as Type 1 tasks)"
- while what needs to be taught to meet higher order objectives (Apply, Create, Evaluate, Analyze) are "==concepts, patterns and relationships== (or what Borich refers to as Type 2 tasks) “.
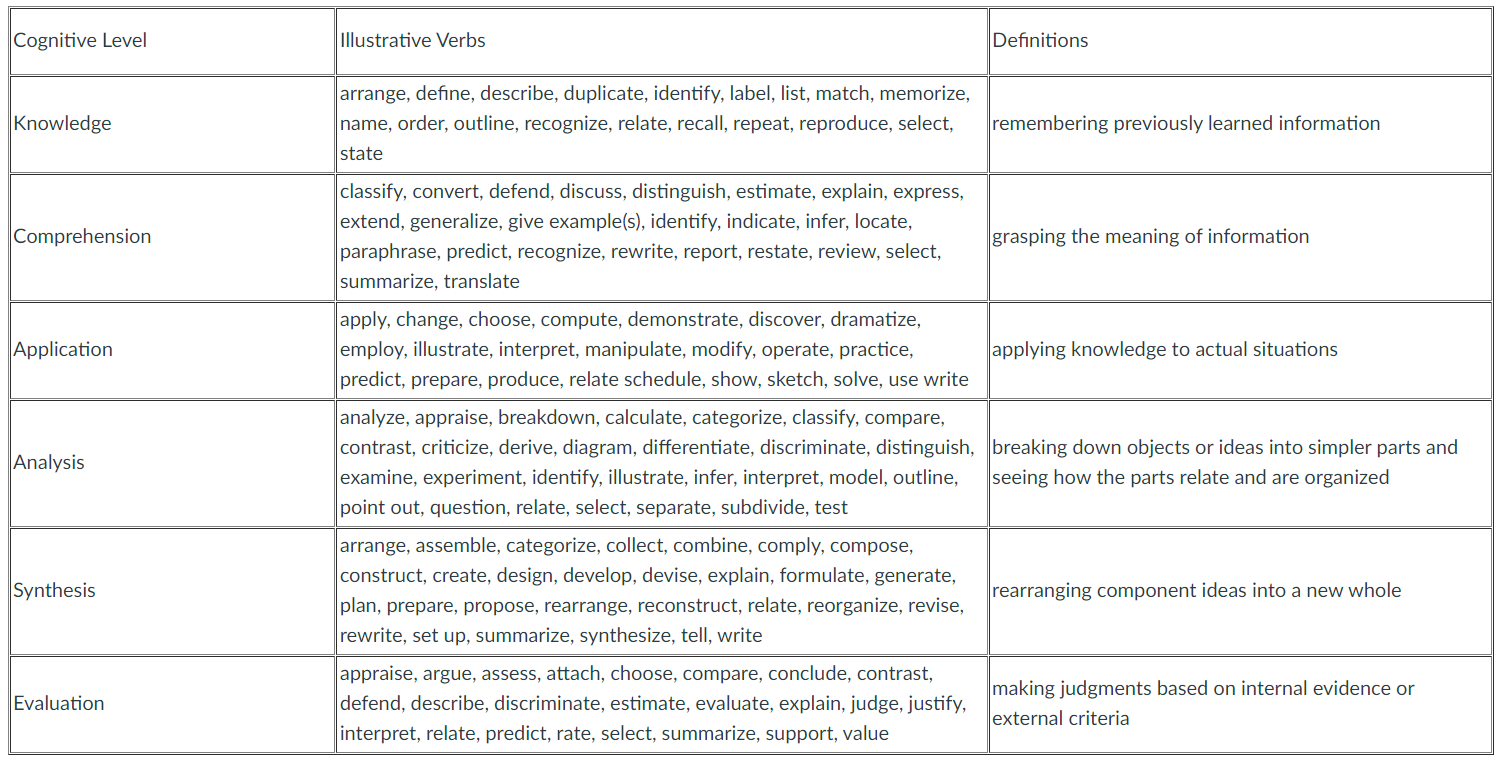
# LO Verbs